Description
Modern mass spectrometers can detect thousands of compounds in the biological samples with unprecedented sensitivity. And metabolomics is a technique to compare and discover the different of compounds (metabolites) in different samples. As a study primarily concerned with compounds in organisms, metabolomics is regarded as the most phenotype-reflective omics. One of the most challenging phases in metabolomics analysis is the annotation and identification of the compounds. Although many databases have been created and a huge number of compounds are present, there is not a complete overlap and no uniform naming standards among them, making manual large-scale searching become a highly time-consuming and error-prone task.
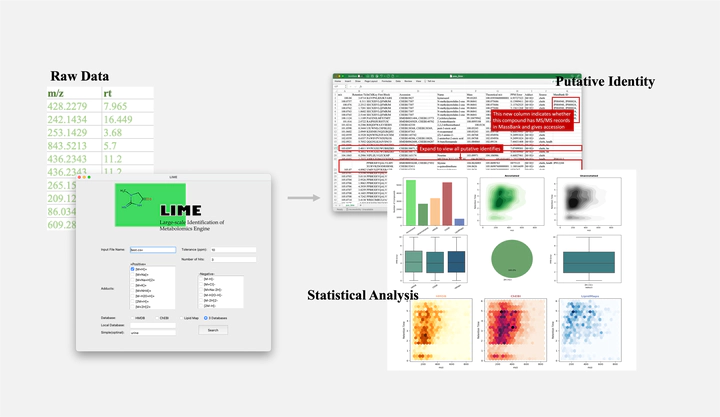
LIME is a high-throughput metabolite annotation tool for post-processed liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) metabolomic data. MS1 Features (m/z, retention time) that uploaded are searched for in LIME-integrated databases and sorted by score. The database of LIME includes 286,268 unique chemical structures when ignoring stereochemistry and charge, which were integrated from Human Metabolome Database (HMDB), Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI), and LIPID MAPS, three mainstream metabolite databases. InChIKey, a fixed-length format derived from IUPAC International Chemical Identifier (InChI) by hash, was used as the unique identifier of LIME.
Input
input file should be a CSV file, first column is m/z, second column is retention time.
Output
Putitave identity table

Statistical analysis

